这篇文章我将介绍 StandardTrie 的简单变体: PatriciaTrie1。
PatriciaTrie或PatriciaTree, 在一些论文中又被称为CompactTrie(紧凑 trie)或CompressedTrie(压缩 trie)。
相关代码:https://github.com/patricklaux/perfect-code
1. 导引
PatriciaTrie 的显著优化是合并单路分支:如果一个非根无值节点有且仅有一个子节点,则将其子节点与该节点合并。
文字描述稍有点抽象,还是看图:
节点合并
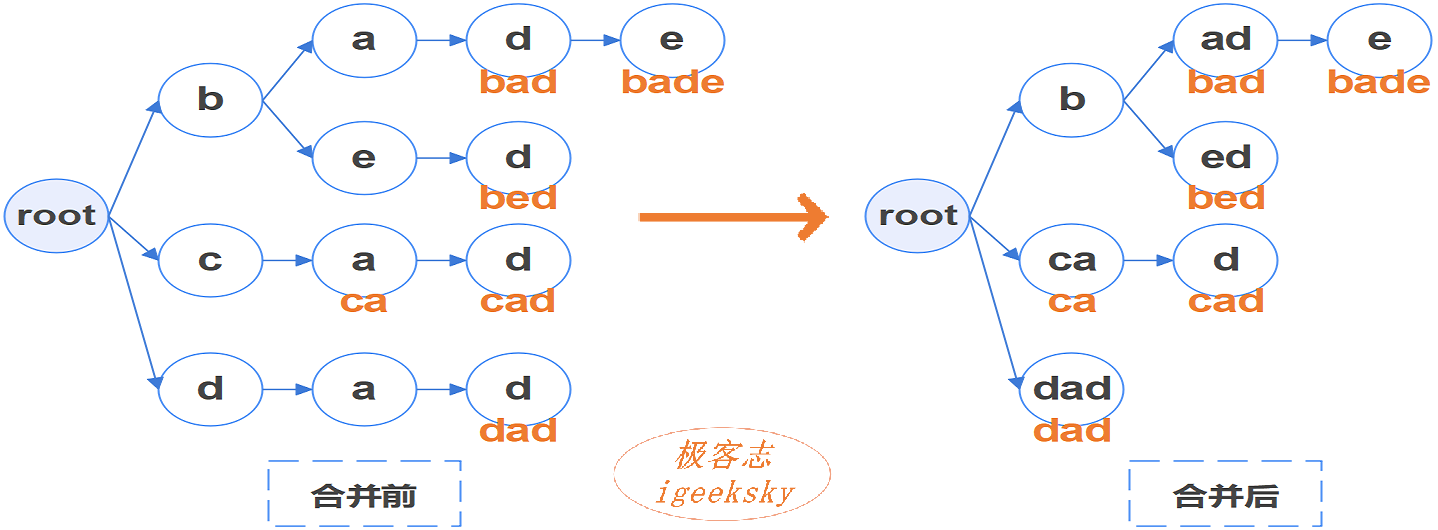
图1:节点合并
节点分裂
如果需要添加键 “da”,该如何来处理哪?我们需要将 “dad” 分裂成两个节点,效果见下图:
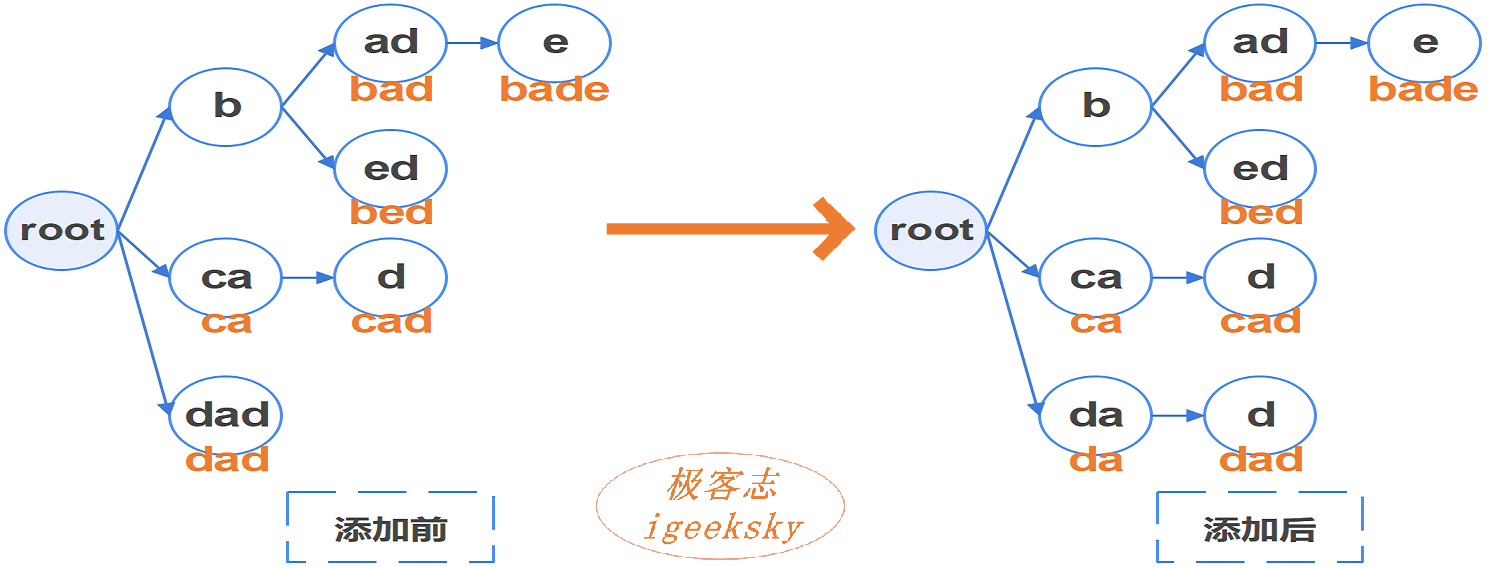
图2:节点分裂
相信,这两张图已足以说明一切😀
同时,我们也可以看到合并后节点数变少,因此减少了可能的内存消耗。
2. 代码实现
依照惯例,还是写代码来实现它。
2.1. 节点定义
package com.igeeksky.perfect.nlp.trie;
private static class PatriciaNode<V> {
// key 的子串
String subKey;
// 值(支持泛型,可以是非字符串)
V val;
// 子节点
PatriciaNode<V>[] table;
public PatriciaNode(int R) {
this.table = new PatriciaNode[R];
}
public PatriciaNode(int R, String subKey) {
this.subKey = subKey;
this.table = new PatriciaNode[R];
}
public PatriciaNode(String subKey, V value) {
this.subKey = subKey;
this.val = value;
}
public PatriciaNode(int R, String subKey, V value) {
this.subKey = subKey;
this.val = value;
this.table = new PatriciaNode[R];
}
}
对比前文的 StandardNode,多了一个 String 类型的 subKey 字段,该字段用于存储节点合并之后的字符串,其它无变化。
2.2. 方法实现
这里继续沿用前文介绍的 Trie 接口(接口介绍见前文)。
2.2.1. 添加键值对
public class PatriciaTrie<V> implements Trie<V> {
private int size;
private static final int R = 65536;
private final PatriciaNode<V> root = new PatriciaNode<>(R);
/**
* 添加键值对
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
*/
@Override
public void put(String key, V value) {
int last = key.length() - 1;
if (last < 0) {
return;
}
PatriciaNode<V> node = root;
for (int i = 0; i <= last; i++) {
char c = key.charAt(i);
// 判断数组是否为空,如果为空则创建数组
if (node.table == null) {
node.table = new PatriciaNode[R];
}
// 通过字符查找子节点,如果子节点不存在则创建子节点并返回,否则与子节点进行字符串比较
PatriciaNode<V> child = node.table[c];
if (child == null) {
node.table[c] = new PatriciaNode<>(key.substring(i), value);
++size;
return;
}
String subKey = child.subKey;
int subLast = subKey.length() - 1;
// 与子节点进行字符串比较
for (int j = 0; j <= subLast; j++, i++) {
// 字符相同
if (subKey.charAt(j) == key.charAt(i)) {
if (i == last) {
if (j == subLast) {
// 直到最后一个字符都完全相同,无需分裂
if (child.val == null) {
++size;
}
child.val = value;
} else {
// 新增键较短,子节点分裂成两个节点,无新的分支节点,例:原有 bcd,新增键bc ——> bc, d
PatriciaNode<V> child0 = new PatriciaNode<>(R, subKey.substring(0, j + 1), value);
node.table[c] = child0;
child.subKey = subKey.substring(j + 1);
child0.table[child.subKey.charAt(0)] = child;
++size;
}
return;
}
if (j == subLast) {
break;
}
} else {
// 字符不同
// 子节点分裂成两个节点,再加上新的分支节点,例:原有 bcd,新增键 bca ——> bc, d, 新分支a
PatriciaNode<V> child0 = new PatriciaNode<>(R, subKey.substring(0, j));
node.table[c] = child0;
child.subKey = subKey.substring(j);
child0.table[child.subKey.charAt(0)] = child;
// 新分支
PatriciaNode<V> child1 = new PatriciaNode<>(key.substring(i), value);
child0.table[child1.subKey.charAt(0)] = child1;
++size;
return;
}
}
node = child;
}
}
}
对比 StandardTrie,代码稍微复杂了一些,多了与子节点进行字符比较的逻辑。另外,从代码也可以看出,其时间复杂度依然是 O(m),m 为字符串长度。简单画了张图来描述这部分新增逻辑:
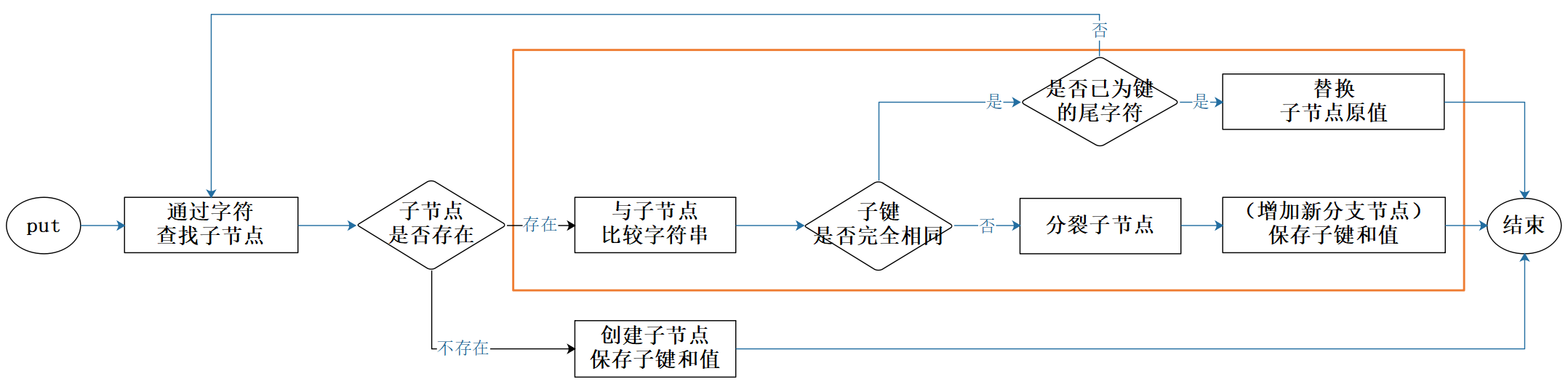
图3:PatriciaTrie put方法
注:与子节点进行字符串比较的逻辑其实可以放到
PatriciaNode中,这样代码会更加清晰可读。因需与前文比对新增逻辑,所以还是放在了这里。
2.2.2. 查找和删除
public class PatriciaTrie<V> implements Trie<V> {
/**
* 获取键关联的值
*
* @param key 键
* @return 值
*/
@Override
public V get(String key) {
PatriciaNode<V> node = find(key);
return (node == null) ? null : node.val;
}
/**
* 通过键查找节点
*
* @param key 键
* @return 键的对应节点
*/
private PatriciaNode<V> find(String key) {
int last = key.length() - 1;
if (last < 0) {
return null;
}
PatriciaNode<V> node = root;
for (int i = 0; i <= last; i++) {
if (node.table == null || (node = node.table[key.charAt(i)]) == null) {
return null;
}
String subKey = node.subKey;
int subLast = subKey.length() - 1;
for (int j = 0; j <= subLast; j++, i++) {
if (subKey.charAt(j) == key.charAt(i)) {
if (i == last) {
if (j == subLast) {
return node;
}
return null;
}
if (j == subLast) {
break;
}
continue;
}
return null;
}
}
return node;
}
/**
* 删除键值对(惰性删除)
*
* @param key 键
* @return 旧值
*/
@Override
public V remove(String key) {
PatriciaNode<V> node = find(key);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
V oldVal = node.val;
if (oldVal != null) {
// 惰性删除:仅把关联的值置空,没有真正删除节点
node.val = null;
--size;
}
return oldVal;
}
}
2.2.3. 前缀匹配
输入一个字符串,返回树中匹配的最长前缀。
/**
* 前缀匹配:查找 word 的最长前缀
*
* @param word 待匹配词(不为空且长度大于0)
* @return 键值对
*/
@Override
public Tuple2<String, V> prefixMatch(String word) {
int last = word.length() - 1;
if (last < 0) {
return null;
}
PatriciaNode<V> node = root;
Tuple2<String, V> tuple2 = null;
for (int i = 0; i <= last; i++) {
if (node.table == null || (node = node.table[word.charAt(i)]) == null) {
return tuple2;
}
String subKey = node.subKey;
int subLast = subKey.length() - 1;
for (int j = 0; j <= subLast; j++, i++) {
if (subKey.charAt(j) == word.charAt(i)) {
if (j == subLast) {
if (node.val != null) {
tuple2 = Tuples.of(word.substring(0, i + 1), node.val);
}
break;
}
if (i == last) {
return tuple2;
}
continue;
}
return tuple2;
}
}
return tuple2;
}
2.2.4. 前缀搜索
输入一个字符串,返回树中所有以该字符串为前缀的键值对。
/**
* 查找并返回以 prefix 开头的所有键(及关联的值)
*
* @param prefix 前缀(不为空且长度大于0)
* @return 所有以 prefix 开头的键值对
*/
@Override
public List<Tuple2<String, V>> keysWithPrefix(String prefix) {
List<Tuple2<String, V>> results = new LinkedList<>();
PatriciaNode<V> parent = find(prefix);
if (parent == null) {
return results;
}
traversal(parent, prefix, results);
return results;
}
/**
* 深度优先遍历,将所有以 prefix 开头的键值对添加到结果集
*
* @param parent 父节点
* @param prefix 前缀
* @param results 结果集
*/
private void traversal(PatriciaNode<V> parent, String prefix, List<Tuple2<String, V>> results) {
if (parent.val != null) {
results.add(Tuples.of(prefix, parent.val));
}
if (parent.table != null) {
for (int c = 0; c < R; c++) {
// 由于数组中可能存在大量空链接,因此遍历时可能会有很多无意义操作
PatriciaNode<V> node = parent.table[c];
if (node != null) {
String key = prefix + node.subKey;
traversal(node, key, results);
}
}
}
}
2.2.5. 包含匹配
输入一段文本,判断该文本是否包含树中的键,如果有,则返回键、值及起止位置(可能有多个)。
/**
* 查找给定文本段中包含的键
*
* @param text 文本段(不为空且长度大于0)
* @return 结果集(键、值、起止位置)
*/
@Override
public List<Found<V>> matchAll(String text) {
List<Found<V>> results = new LinkedList<>();
int last = text.length() - 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= last; i++) {
matchAll(results, text, i, last);
}
return results;
}
/**
* 找到前缀节点后,遍历所有后缀节点,并将所有后缀节点包含的键值对添加到结果集
*
* @param results 结果集
* @param text 文本段
* @param start 文本段的开始位置
* @param last 文本段的结束位置(末尾)
*/
private void matchAll(List<Found<V>> results, String text, int start, int last) {
PatriciaNode<V> node = root;
for (int i = start; i <= last; i++) {
if (node.table == null || (node = node.table[text.charAt(i)]) == null) {
return;
}
String subKey = node.subKey;
int subLast = subKey.length() - 1;
for (int j = 0; j <= subLast; j++, i++) {
if (subKey.charAt(j) == text.charAt(i)) {
if (j == subLast) {
if (node.val != null) {
results.add(new Found<>(start, i, text.substring(start, i + 1), node.val));
}
break;
}
if (i == last) {
return;
}
continue;
}
return;
}
}
}
PatriciaTrie 的逻辑还是比较简单的,相关代码和测试用例都在这里 perfect-code,有兴趣可拉取代码进行调试。
3. 性能分析
3.1. 时间、空间与动态更新
- 动态更新:依然支持运行期间动态更新数据。
- 时间性能:依然只跟字符串的长度 m 相关,且其时间复杂度最好和最坏的情况都是 O(m)。
- 空间性能:减少了单分支节点的创建,但依然需要创建大量固定容量为 R 的数组,还是可能存在大量空链接。
4. 相关说明
Patricia 的全称是 “检索字母数字编码信息的实用算法“(practical algorithm to retrieve information coded in alphanumeric),于1968年 由 Morrison 发明,是基于二进制位比较方式的实现。
《Algorithms in c, 3ed》2 详细描述了 Patricia Trie 二进制位比较方式的实现,并简单介绍了字符比较方式。
《The Art of Computer Programming. Volume III: Sorting and Searching》3 介绍了二进制位比较方式。
斯坦福的 cs166 课程4 和卡尔顿大学的 Comp5408 课程5 也讲解了 Patricia Trie ,这两者都是基于字符比较方式。
NIST6 给出了 Patricia Trie 的名词解释,似乎比维基百科的词条要准确。
5. 参考资料
Morrison, Donald R.. “PATRICIA—Practical Algorithm To Retrieve Information Coded in Alphanumeric.” Journal of the ACM 15 (1968): 514 - 534. ↩︎
R. Sedgewick. “Algorithms in C, third edition.” Addison-Wesley(1998):614-648 ↩︎
Donald E. Knuth. “The Art of Computer Programming. Volume III: Sorting and Searching.” Addison-Wesley(1973):492-512 ↩︎
http://web.stanford.edu/class/cs166/lectures/16/Slides16.pdf ↩︎